Collins Laboratory
Background
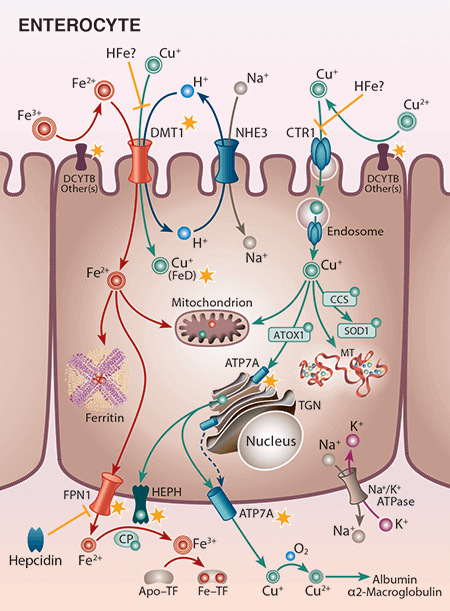
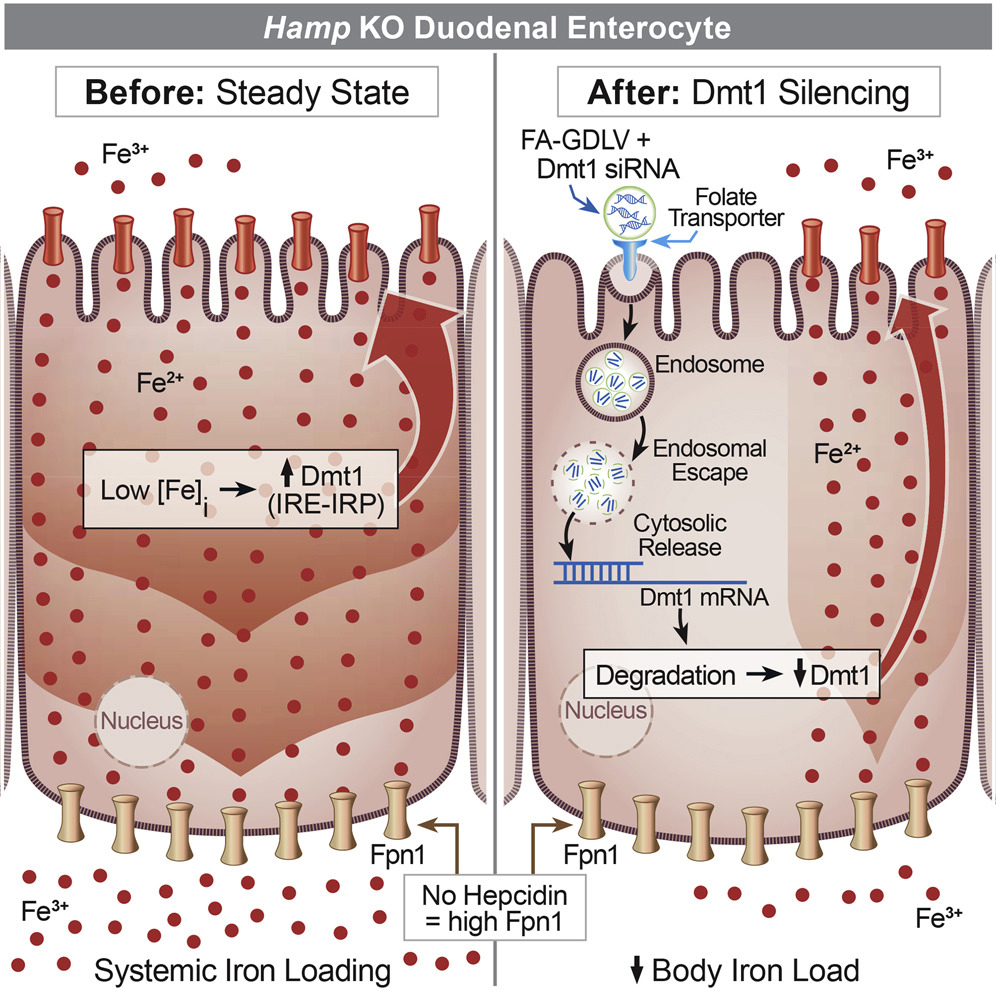
Dr. Collins has broad training and expertise in physiology, molecular biology, genetics, and nutrition, and he has been involved in biomedical research for over 25 years. His formal post-baccalaureate educational training includes master’s studies in molecular biology, doctoral studies in molecular physiology at Vanderbilt University and post-doctoral work in transport physiology at the University of Arizona. Dr. Collins’ research previously focused on molecular aspects of intestinal sodium and phosphate absorption, but more recently, over the past 15 years or so, his research efforts have shifted to the investigation of iron metabolism and how this is influenced by copper, with a particular focus on mechanisms of intestinal transport of these essential nutrients. This is an important area of research, as body iron homeostasis, unlike most other nutrients, is controlled principally at the level of intestinal absorption since no active excretory systems exist in humans or other mammals. Studies over the past 10+ years have identified copper-dependent aspects of intestinal iron transport. Ongoing studies relate to iron supplementation and how this negatively impacts copper homeostasis (e.g. in pregnancy), and to development of therapeutic approaches to modulate intestinal iron absorption in various disease states (e.g., hereditary hemochromatosis and β-thalassemia). Model systems include wild-type and genetically engineered (knockout) laboratory mice and rats, as well as surgical human intestinal tissues. Commonly used experimental techniques include molecular biology methods such as qRT-PCR and western blotting, radiotracer iron and copper absorption studies (by oral, intragastric gavage), quantification of iron in blood and tissues (using various methods including ICP-MS), a variety of physiological techniques, and Ussing chamber analysis to determine mechanistic (and kinetic) aspects of nutrient absorption. The Collins laboratory is staffed predominantly by Nutritional Sciences doctoral students, several of whom have graduated over the past few years. Funding for his work has been competitively awarded by the National Institutes of Health (NIDDK, ODS) for the past 15+ years.